Advertisement
TYPES OF CENTRIFUGAL PUMPS
Advertisement
Centrifugal pumps can be categorised in various ways. Some of the main types are on the following basis:
Advertisement
Orientation of the pump shaft axis:
- This refers to the plane on which the shaft axis of the pump is placed. It is either horizontal or vertical
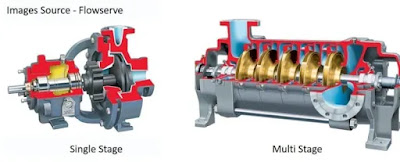
Number of stages:
Advertisement
- This refers to the number of sets of impellers and diffusers in a pump. A set forms a stage and it is usually single, dual, or multiple (more than two) stages.
Suction flange orientation:
Advertisement
- This is based on the orientation of the pump suction flange. This orientation could be horizontal (also known as End) or vertical (also known as Top).
Casing split:
- This classification is based on the casing split. It is either Radial (perpendicular to shaft axis) or Axial (plane of the shaft axis).
Bearing support:
- This is judged based on the location of the bearings supporting the rotor. If the rotor is supported in the form of a cantilever it is called as an Overhung type of pump.
- When the impellers on the rotor are supported with bearings on either side, the pump is called as an in-between bearings pump.
Pump support:
- This refers to how the pump is supported on the base frame. It could be a center-line support or foot-mounted support.
Advertisement
Shaft connection:
- The closed coupled pumps are characterized by the absence of a coupling between the motor and the pump.
- The motor shaft has an extended length and the impeller is mounted on one end.
- The vertical monoblock pumps have the suction and discharge flanges along one axis and can be mounted between pipelines. They are also termed as ‘in-line pumps’.
Sealless pumps:
- Pumps are used to build the pressure in a liquid and if necessary to contain it within the casing. At the interface of the rotating shaft and the pump casing, mechanical seals are installed to do the job of product containment. However, seals are prone to leakages and this maybe unacceptable in certain critical applications. To address this issue, sealless pumps have been designed and manufactured.
These are of two types – canned and magnetic drive pumps:
Advertisement
1. Canned pumps: In the construction of this second type of sealless pump, the rotor comprises of an impeller, shaft, and the rotor of the motor. These are housed within the pump casing and a containment shell . The hazardous or the toxic liquid is confined within this shell and casing. The rotating flux generated by the stator passes through the containment
shell and drives the rotor and the impeller.
2. Magnetic drive pumps: In magnetic drive pumps, the rotor comprises of an impeller, shaft, and driven magnets. These housed within the pump casing and the containment shell ensures that the usually hazardous/toxic liquid is
contained within a metal shell. The driven magnets take their drive from the rotating drive magnets, which are assembled on a different shaft that is coupled to the prime mover.






Post a Comment